Height rank
Rose Rayhaan by Rotana
Dubai
- CTBUH Drawing
- Facts
-
Metrics
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
To Tip:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the highest point of the building, irrespective of material or function of the highest element (i.e., including antennae, flagpoles, signage and other functional-technical equipment).Architectural:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the architectural top of the building, including spires, but not including antennae, signage, flag poles or other functional-technical equipment. This measurement is the most widely utilized and is employed to define the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat (CTBUH) rankings of the "World's Tallest Buildings."Occupied:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the highest occupied floor within the building.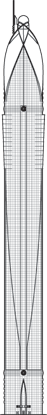
Above Ground
The number of floors above ground should include the ground floor level and be the number of main floors above ground, including any significant mezzanine floors and major mechanical plant floors. Mechanical mezzanines should not be included if they have a significantly smaller floor area than the major floors below. Similarly, mechanical penthouses or plant rooms protruding above the general roof area should not be counted. Note: CTBUH floor counts may differ from published accounts, as it is common in some regions of the world for certain floor levels not to be included (e.g., the level 4, 14, 24, etc. in Hong Kong).Below Ground
The number of floors below ground should include all major floors located below the ground floor level.Official Name
Rose Rayhaan by Rotana
Other Names
Rose Rotana Tower
Type
Building
Status
Completed
Completion
2007
Country
City
Address
Function
A mixed-use tall building contains two or more functions (or uses), where each of the functions occupy a significant proportion of the tower's total space. Support areas such as car parks and mechanical plant space do not constitute mixed-use functions. Functions are denoted on CTBUH "Tallest Building" lists in descending order, e.g., "hotel/office" indicates hotel function above office function.
Hotel
Structural Material
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from steel. Note that a building of steel construction with a floor system of concrete planks or concrete slab on top of steel beams is still considered an “all-steel” structure as the concrete elements are not acting as the primary structure.
All-Concrete
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from concrete which has been cast in place and utilizes steel reinforcement bars and/or steel reinforced concrete which has been precast as individual components and assembled together on-site.
All-Timber
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from timber. An all-timber structure may include the use of localized non-timber connections between timber elements. Note that a building of timber construction with a floor system of concrete planks or concrete slab on top of timber beams is still considered an “all-timber” structure as the concrete elements are not acting as the primary structure.
Mixed-Structure
Utilizes distinct systems (e.g. all-steel, all-concrete, all-timber), one on top of the other. For example, a Steel Over Concrete indicates an all-steel structural system located on top of an all-concrete structural system, with the opposite true of Concrete Over Steel.
Composite
A combination of materials (e.g. steel, concrete, timber) are used together in the main structural elements. Examples include buildings which utilize: steel columns with a floor system of reinforced concrete beams; a steel frame system with a concrete core; concrete-encased steel columns; concrete-filled steel tubes; etc. Where known, the CTBUH database breaks out the materials used within a composite building’s primary structural elements.
Concrete-Steel Composite
Height
333 m / 1,093 ft
Floors Above Ground
71
Floors Below Ground
1
# of Hotel Rooms
684
# of Elevators
8
Top Elevator Speed
4 m/s
Tower GFA
50,569 m² / 544,320 ft²
Rankings
-
By function
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
-
By material
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Construction Schedule
Construction Start
Completed
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Developer
BONYAN International Investment Group L.L.C.
Architect
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Khatib & Alami
Structural Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Khatib & Alami
MEP Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Khatib & Alami
Contractor
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Arabian Construction Company
Other Consultant
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
Aluminium and Light Industries Company Ltd
BMT Fluid Mechanics Ltd.
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
CTBUH Initiatives
Top Company Rankings: The World’s 100 Tallest Buildings
13 October 2016 - CTBUH Research
Research
31 January 2019
Interactive Study on Tall Buildings in Numbers: 2018 Year in Review
CTBUH Research
In 2018, 143 buildings of 200 meters’ height or greater were completed. This is a slight decrease from 2017’s record-breaking total of 147, and it...
About Rose Rayhaan by Rotana
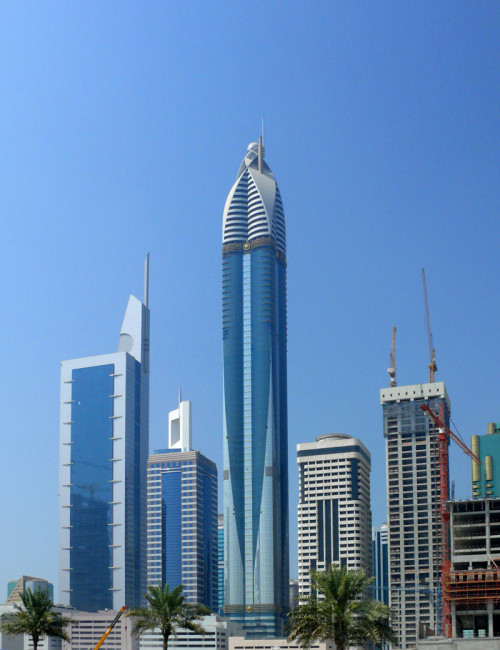
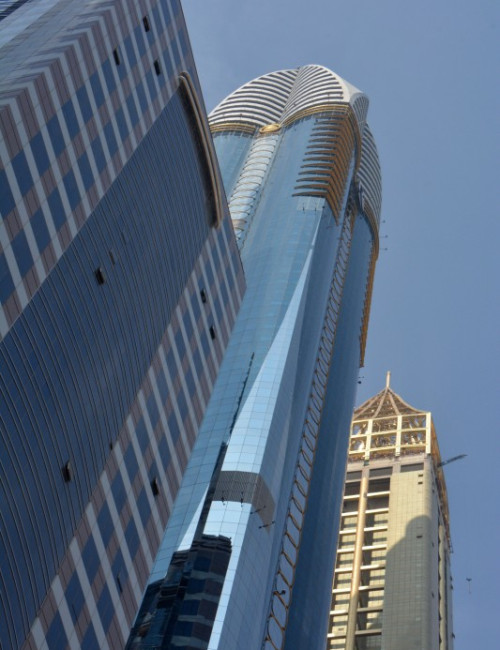
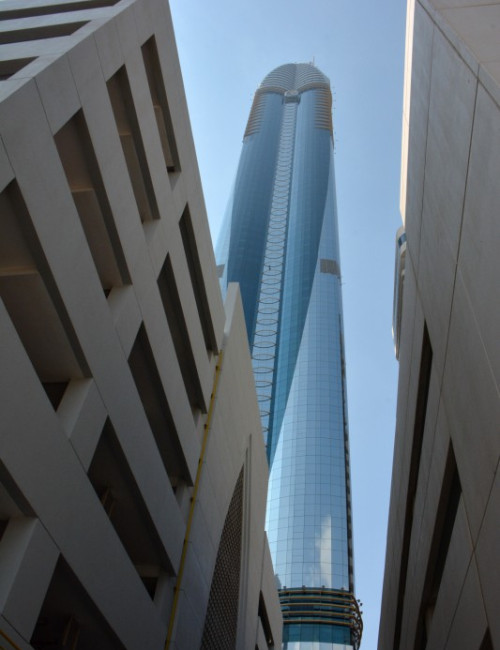
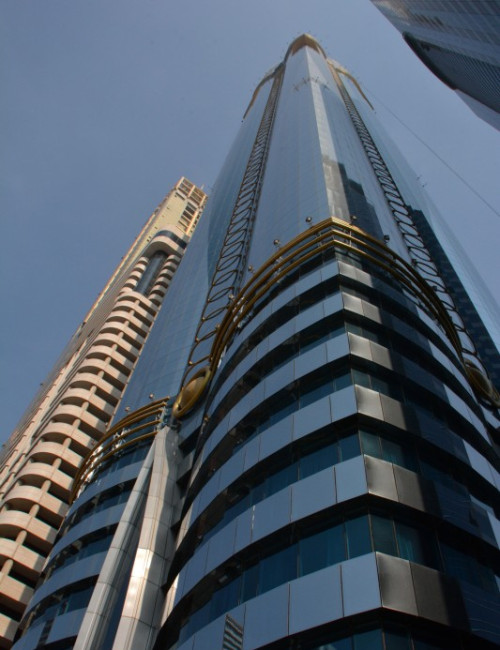
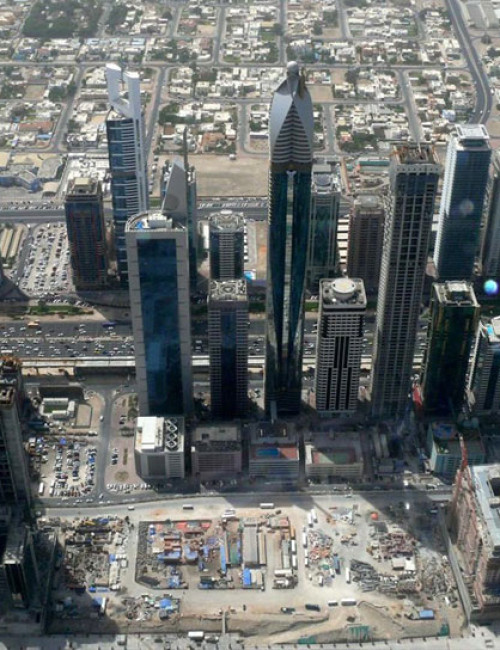
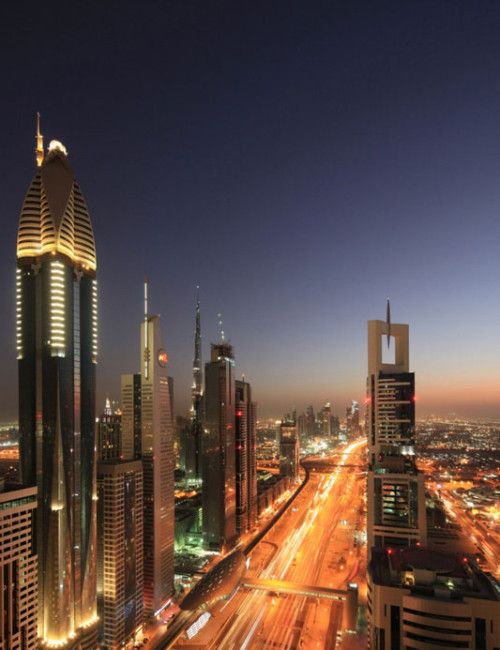
Rose Rayhaan by Rotana is a supertall hotel on Sheikh Zayed Road in Dubai’s financial district. The original plans were for the tower to reach 380 meters, but the design was later modified to reduce the height of the tower.
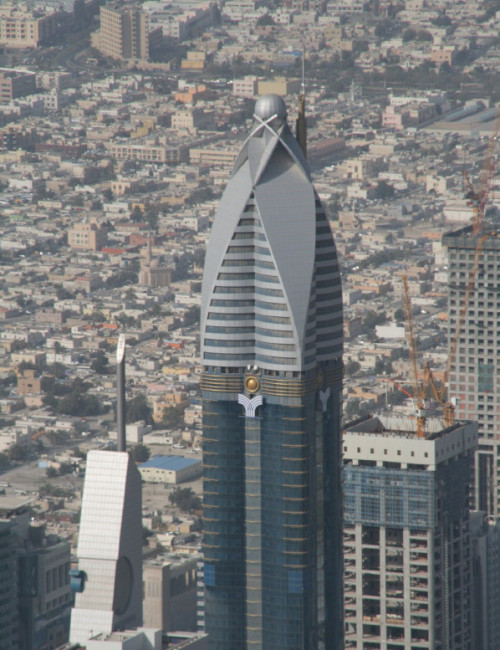
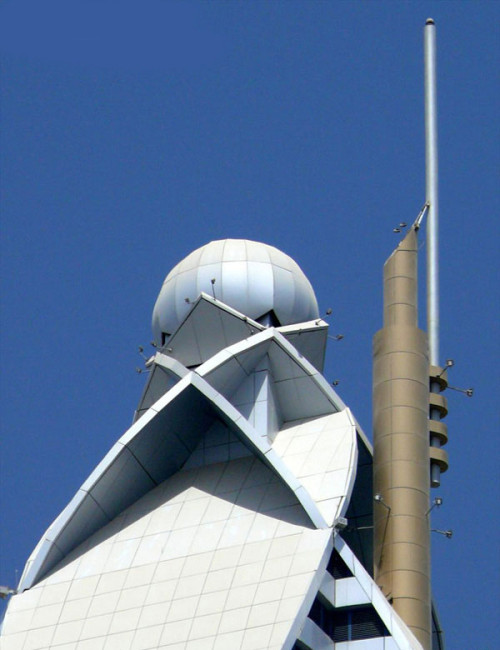
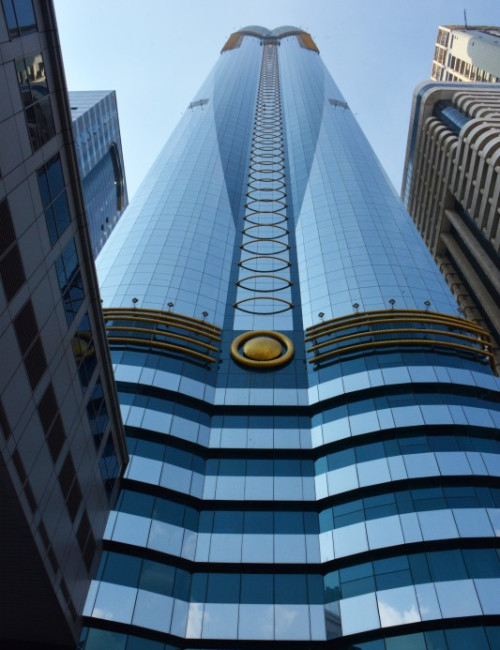
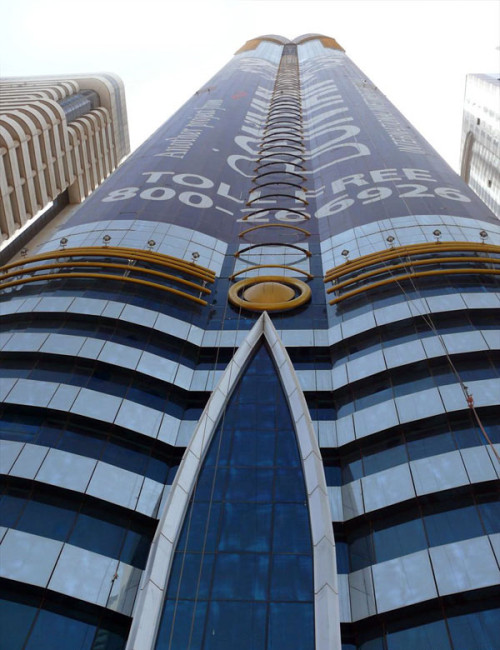
The hotel’s form is stylistically varied. The highly embellished façade is composed of two tones of blue and silver mirrored glass with gold ornamentation. A narrow panel of oculiform gold rings stretches up the center of each elevation. Each side of the tower incorporates two convex cylindrical forms that fold into one another. Façade sections flatten towards the top and reach up into an elaborate sculptural peak of intersecting petals, a visual reference to the building’s informal name, “The Rose.” This floral element crowning the tower is topped by a sphere. A spire extending up from the roof is the ultimate pinnacle of the tower.
The hotel also considers the multitude of business travelers who pass through Dubai, and thus features professional event space, conference rooms, and an auditorium. The Tower offers guests a choice of 482 rooms, suites, and penthouses. Marble and glass adorn the lobby on the ground floor. On offer for hotel guests are a fully equipped gymnasium, outdoor temperature-controlled swimming pools for adults and children, Jacuzzi, steam room, and massage rooms. The high-degree of luxury offered reflects the building’s position as a world-class hotel in an international city.
Research

31 January 2019
Interactive Study on Tall Buildings in Numbers: 2018 Year in Review
CTBUH Research
In 2018, 143 buildings of 200 meters’ height or greater were completed. This is a slight decrease from 2017’s record-breaking total of 147, and it...

31 December 2007
Tallest Buildings Completed in 2007
333 meters high with 72 stories and 480 suites, Rose Rotana Tower in Dubai leads the list of the 10 tallest buildings completed in 2007....
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy

























