Height rank
Keangnam Hanoi Landmark Tower
Hanoi
- CTBUH Drawing
- Facts
-
Metrics
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
To Tip:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the highest point of the building, irrespective of material or function of the highest element (i.e., including antennae, flagpoles, signage and other functional-technical equipment).Architectural:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the architectural top of the building, including spires, but not including antennae, signage, flag poles or other functional-technical equipment. This measurement is the most widely utilized and is employed to define the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat (CTBUH) rankings of the "World's Tallest Buildings."Occupied:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the highest occupied floor within the building.
Above Ground
The number of floors above ground should include the ground floor level and be the number of main floors above ground, including any significant mezzanine floors and major mechanical plant floors. Mechanical mezzanines should not be included if they have a significantly smaller floor area than the major floors below. Similarly, mechanical penthouses or plant rooms protruding above the general roof area should not be counted. Note: CTBUH floor counts may differ from published accounts, as it is common in some regions of the world for certain floor levels not to be included (e.g., the level 4, 14, 24, etc. in Hong Kong).Below Ground
The number of floors below ground should include all major floors located below the ground floor level.Official Name
Keangnam Hanoi Landmark Tower
Other Names
Landmark 72
Name of Complex
Type
Building
Status
Completed
Completion
2012
Country
City
Address
Function
A mixed-use tall building contains two or more functions (or uses), where each of the functions occupy a significant proportion of the tower's total space. Support areas such as car parks and mechanical plant space do not constitute mixed-use functions. Functions are denoted on CTBUH "Tallest Building" lists in descending order, e.g., "hotel/office" indicates hotel function above office function.
Hotel / Residential / Office
Structural Material
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from steel. Note that a building of steel construction with a floor system of concrete planks or concrete slab on top of steel beams is still considered an “all-steel” structure as the concrete elements are not acting as the primary structure.
All-Concrete
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from concrete which has been cast in place and utilizes steel reinforcement bars and/or steel reinforced concrete which has been precast as individual components and assembled together on-site.
All-Timber
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from timber. An all-timber structure may include the use of localized non-timber connections between timber elements. Note that a building of timber construction with a floor system of concrete planks or concrete slab on top of timber beams is still considered an “all-timber” structure as the concrete elements are not acting as the primary structure.
Mixed-Structure
Utilizes distinct systems (e.g. all-steel, all-concrete, all-timber), one on top of the other. For example, a Steel Over Concrete indicates an all-steel structural system located on top of an all-concrete structural system, with the opposite true of Concrete Over Steel.
Composite
A combination of materials (e.g. steel, concrete, timber) are used together in the main structural elements. Examples include buildings which utilize: steel columns with a floor system of reinforced concrete beams; a steel frame system with a concrete core; concrete-encased steel columns; concrete-filled steel tubes; etc. Where known, the CTBUH database breaks out the materials used within a composite building’s primary structural elements.
All-Concrete
Height
328.6 m / 1,078 ft
Floors Above Ground
72
Floors Below Ground
2
# of Apartments
300
# of Hotel Rooms
383
Top Elevator Speed
7 m/s
Rankings
-
By function
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
-
By material
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Construction Schedule
Construction Start
Completed
Architect
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Structural Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Project Manager
The CTBUH lists a project manager when a specific firm has been commissioned to oversee this aspect of a tall building’s design/construction. When the project management efforts are handled by the developer, main contract, or architect, this field will be omitted.
The CTBUH lists a project manager when a specific firm has been commissioned to oversee this aspect of a tall building’s design/construction. When the project management efforts are handled by the developer, main contract, or architect, this field will be omitted.
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Owner
AON Holdings
Qatar Investment Authority
Architect
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Heerim Architects & Planners; HOK, Inc.; Samoo Architects & Engineers
Structural Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Project Manager
The CTBUH lists a project manager when a specific firm has been commissioned to oversee this aspect of a tall building’s design/construction. When the project management efforts are handled by the developer, main contract, or architect, this field will be omitted.
The CTBUH lists a project manager when a specific firm has been commissioned to oversee this aspect of a tall building’s design/construction. When the project management efforts are handled by the developer, main contract, or architect, this field will be omitted.
Contractor
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Keangnam Enterprise
Other Consultant
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
BMT Fluid Mechanics Ltd.
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Videos

03 March 2008 | Hanoi
Sustainable Design in South Korea and Vietnam
Matthias A. Olt & James P. Rothwell of Callison, discussed two high-rise towers in South Korea and Vietnam at the CTBUH 8th World Congress in...
Research

01 September 2017
Application of Post-Tension Technology on Tall Buildings
Kwangryang Chung, Jungwoo Park & Younghye Kim, Dong Yang Structural Engineers Co., Ltd; Dohun Kim, POSCO E&C
It’s been a decade since post-tension system began to be applied in earnest to buildings in Korea. In the meantime, posttension system has been used...
About Keangnam Hanoi Landmark Tower
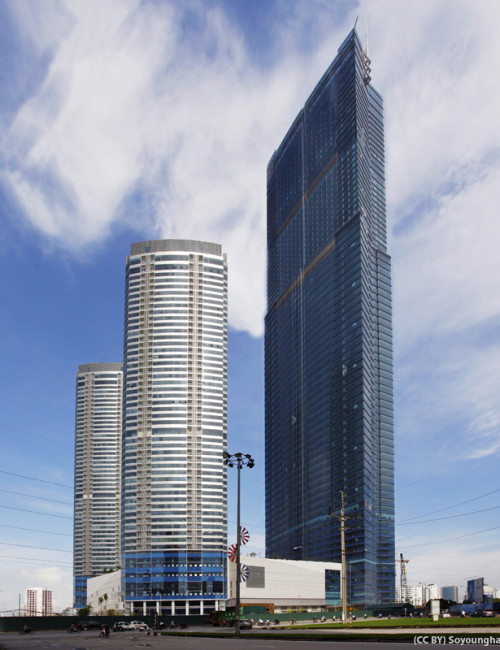
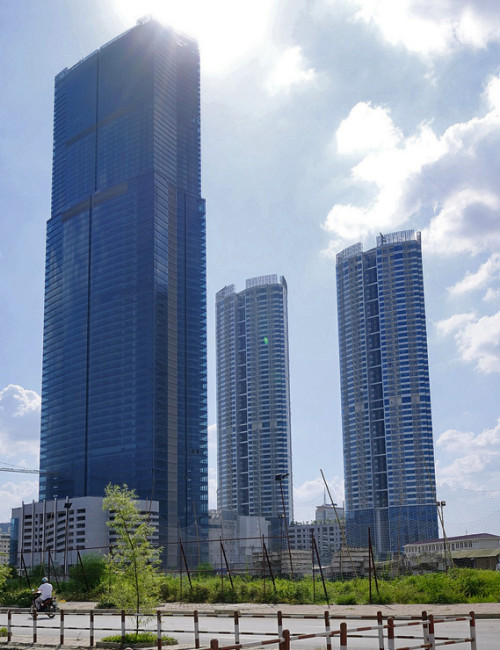
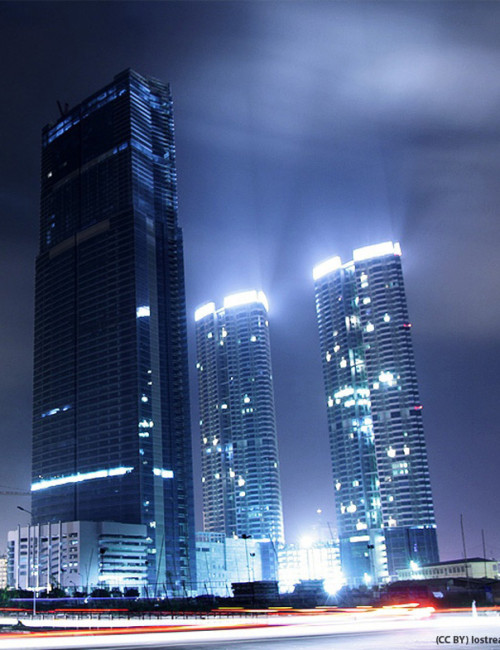
Upon completion in 2012, Keangnam Hanoi Landmark Tower was the tallest building in Vietnam and was a redefining moment for the city of Hanoi, which at the time had very few tall buildings. The 72 story building is comprised of offices and is the tallest in a three building complex featuring two 49 story residential towers with curved facades to maximize views. While the complex is located on the western edge of the city, the placement positions the development within the center of a newly established central business district.
In order to construct the complex in the soft soils of Hanoi, 980 piles with diameters of up to two meters across were drilled deep underground in a process which took longer than one full year during the construction phase. The reinforced concrete frame of the 72 story tower utilized post-tensioning which allowed the structure to rise as quickly as of one floor every five days, a rate which is faster than what would have occurred with conventional construction techniques. Cladding the tower is a double glazed façade, producing a desired modern aesthetic for the exterior which combined with an intelligent building systems technology, provides a high level of energy efficiency. At the peak of construction, the worksite employed as many as 8000 people at one time.
The base of the Keangnam Hanoi Landmark Tower is attached to a shared podium structure containing shops, a department store and a cinema from which all three towers then rise. The main tower then is comprised of offices on floors 12-46, serviced apartments on floors 48-60 and a full service hotel on floors 62-70. The uppermost 72nd floor contains an observatory with a panoramic view of Hanoi and its rapidly growing skyline.
Research

01 September 2017
Application of Post-Tension Technology on Tall Buildings
Kwangryang Chung, Jungwoo Park & Younghye Kim, Dong Yang Structural Engineers Co., Ltd; Dohun Kim, POSCO E&C
It’s been a decade since post-tension system began to be applied in earnest to buildings in Korea. In the meantime, posttension system has been used...

31 December 2012
Year in Review: Tall Trends of 2012
Kevin Brass, Antony Wood & Marty Carver, CTBUH
For the first time in six years the number of tall buildings completed annually around the world declined as the effects of the global financial...
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy








