Filter by
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Forum 66 Tower 1
Conard Shenyang, Conrad Shenyang, Hang Lung Plaza Tower 1
Building
Completed
2015
Hotel / Office
Concrete-Steel Composite
LEED Silver
350.6 m / 1,150 ft
68
4
315
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Construction Start
Completed
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The CTBUH lists a project manager when a specific firm has been commissioned to oversee this aspect of a tall building’s design/construction. When the project management efforts are handled by the developer, main contract, or architect, this field will be omitted.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Usually takes on the balance of the architectural effort not executed by the "Design Architect," typically responsible for the construction documents, conforming to local codes, etc. May often be referred to as "Executive," "Associate," or "Local" Architect, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Architect of Record" exclusively.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The CTBUH lists a project manager when a specific firm has been commissioned to oversee this aspect of a tall building’s design/construction. When the project management efforts are handled by the developer, main contract, or architect, this field will be omitted.
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
2016 CTBUH Awards
13 October 2016 - CTBUH Research
13 May 2016 - Awards Conference
Ermell_ccbysa.jpg)
19 January 2016
Jason Gabel, Marty Carver & Marshall Gerometta, CTBUH
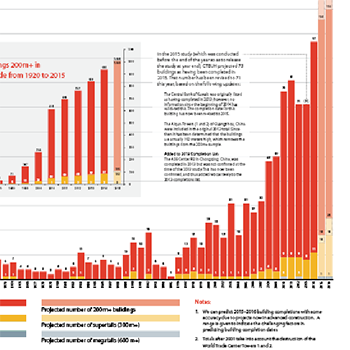
CTBUH has determined that 106 buildings of 200 meters’ height or greater were completed around the world in 2015 – setting a new record for...
The design for Forum 66, a new mixed-use development in Shenyang, creates a daring new icon for one of northeast China’s most exciting and rapidly growing cities. Situated at the south side of City Plaza on the area’s main artery, Qing Nian Da Jie, the Forum 66 site is one of the most desirable locations in the city. The centrally located development, which includes office towers, a hotel, apartments, and a retail mall, is intended to drive energy and commerce in the surrounding region.
The architectural language of the project is based on the geometry of gentle curves, inspired by the flow of the river from which the city of Shenyang takes its name. The architects’ design features two dynamic office towers at the northern edge of the site, acting as a gateway from City Plaza to the new development and serving to reinforce the edge of the site. Forum 66 Tower 1 was conceived to be part of a family of forms united through the use of a consistent curtain-wall design and featuring angled tops.
These sleek towers are topped by glowing lanterns that appear to be floating, which sparkle during the daytime and light up the sky at night. While the office towers are gently curved in plan, they are very close to the optimal configuration of a rectangle. The proportion of the plan is broad enough to allow for a highly-efficient structural design and thus a minimized column area. The sides of the office towers and hotel that are facing the eye-shaped middle center of the complex taper inward, which enhances a sense of openness and creates an inviting spatial dynamic for the larger complex.
2016 CTBUH Awards
Ermell_ccbysa.jpg)
19 January 2016
Jason Gabel, Marty Carver & Marshall Gerometta, CTBUH
CTBUH has determined that 106 buildings of 200 meters’ height or greater were completed around the world in 2015 – setting a new record for...
31 December 2014
Daniel Safarik, Antony Wood, Marty Carver & Marshall Gerometta, CTBUH
An All-Time Record 97 Buildings of 200 Meters or Higher Completed in 2014 and 2014 showed further shifts towards Asia, and also surprising developments in...
13 October 2016
The Council is pleased to announce the Top Company Rankings for numerous disciplines as derived from the list of projects appearing in 100 of the World’s Tallest Buildings.
13 May 2016
The inaugural CITAB-CTBUH China Tall Building Awards were held at Shanghai Tower culminating with Bund SOHO winning China Best Tall Building Overall Award.
25 February 2016
CITAB and CTBUH are pleased to announce the award recipients for the inaugural CITAB-CTBUH 2016 China Tall Building Awards.
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy