Filter by
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
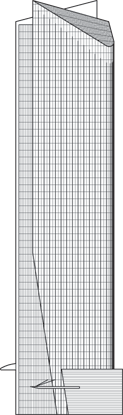
Toranomon Hills Mori Tower
Andaz Tokyo - Toranomon Hills, Loop Road #2 Shimbashi, Toranomon Redevelopment Project Building III, Loop Line 2 - Zone III
Building
Completed
2014
Hotel / Residential / Office
All-Steel
255.5 m / 838 ft
52
5
172
164
49
7 m/s
244,360 m² / 2,630,269 ft²
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Construction Start
Completed
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
2016 CTBUH Awards
22 August 2018 - CTBUH Research
22 June 2016 - Awards

27 October 2015 | Tokyo
A city is a stage where a wide range of activities take place. An internationally competitive city is one in which diverse human interaction and...

26 October 2015
Hiroo Mori, Mori Building Co., Ltd.
Skyscrapers and their surrounding developments are critical factors in determining a city’s global competitive advantage relative to other cities. These building projects are in fact...

02 December 2019
Groundwork on the OMA-designed Toranomon Hills Station Tower in downtown Tokyo officially started on 25 November 2019. The high-rise forms part of Mori Building’s US$3.6...

26 October 2015
Hiroo Mori, Mori Building Co., Ltd.
Skyscrapers and their surrounding developments are critical factors in determining a city’s global competitive advantage relative to other cities. These building projects are in fact...
20 May 2015
Masayoshi Nakai, Takenaka Corporation
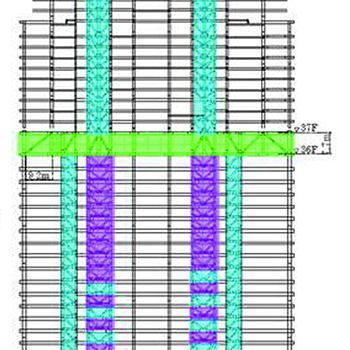
This paper reviews the development and current status of seismic design for high-rise buildings in earthquake-prone Japan. Additionally, it briefly describes two important areas of...

20 May 2015
Hiroo Mori, Roppongi Hills Mori Tower
As host of the 2020 Summer Olympics, Tokyo is undertaking a major redevelopment effort, giving long-planned projects new energy under the political impetus of the...
31 December 2014
Daniel Safarik, Antony Wood, Marty Carver & Marshall Gerometta, CTBUH
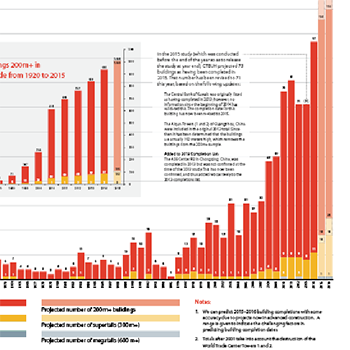
An All-Time Record 97 Buildings of 200 Meters or Higher Completed in 2014 and 2014 showed further shifts towards Asia, and also surprising developments in...

01 September 2014
Yasuyoshi Hitomi, Hiroshi Takahashi, & Hidenori Karasaki, Nihon Sekkei
Toranomon Hills is the main building of a large-scale re-development project located in the center of Tokyo. The remarkable feature of this high-rise building is...
22 August 2018
CTBUH has released a Tall Buildings in Numbers (TBIN) interactive data study on the world's tallest buildings with dampers.
22 June 2016
CTBUH is proud to announce the winners and finalists for the CTBUH 2016 Tall Building Awards, chosen from a pool of 132 submissions vying for recognition.
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy