Filter by
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
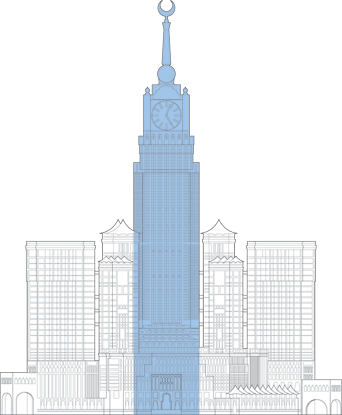
Makkah Royal Clock Tower
Fairmont Makkah Clock Royal Tower, King Abdul Aziz Endowment Tower, Makkah Royal Clock Tower Hotel
Building
Completed
2012
Serviced Apartments / Hotel / Retail
Steel Over Concrete
601 m / 1,972 ft
120
3
858
96
6 m/s
310,638 m² / 3,343,680 ft²
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Proposed
Construction Start
Completed
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Peer Review Engineer traditionally comments on the information produced by another party, and to render second opinions, but not to initiate what the design looks like from the start.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The CTBUH lists a project manager when a specific firm has been commissioned to oversee this aspect of a tall building’s design/construction. When the project management efforts are handled by the developer, main contract, or architect, this field will be omitted.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Peer Review Engineer traditionally comments on the information produced by another party, and to render second opinions, but not to initiate what the design looks like from the start.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The CTBUH lists a project manager when a specific firm has been commissioned to oversee this aspect of a tall building’s design/construction. When the project management efforts are handled by the developer, main contract, or architect, this field will be omitted.
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
28 November 2018 - CTBUH Research
12 September 2017 - CTBUH Research

12 October 2011 | Mecca
The protection of high rise buildings with a state-of-the-art fire suppression system is always considered as a challenge. Conventional sprinkler systems are known for decades...
22 August 2022
Tarek Hassan, Yehia El-Ezaby & Charles Malek, rector Dar Al Handasah Consultants (Shair and Partners)
This paper presents an overview of a process of optimizing concrete mixture for tall buildings, culminating in the design of the Iconic Tower, the key...
At the heart of the holiest Islamic city, Makkah Royal Clock Tower brings an air of modernization to the bustling historic center of Mecca. The tower was developed as a component of the King Abdulaziz Endowment Project and provides comfortable accommodations for devout Muslims that make the journey to the city every year during the Hajj period. It is conveniently located adjacent to the Grand Mosque, which can accommodate up to two million worshippers over the course of the event.
The clock tower stands in the center of a high-rise complex called Abraj Al-Bait. Six smaller high-rises surround it at heights varying and accommodate both residential and hotel uses. True to its name, four colossal clock faces are mounted near the top of the tower. These clocks hold the record for both the largest and highest in the world. At night, the clock faces are illuminated by one million LED lights that transform the tower into a green and white beacon. Writing is inscribed above each clock, with the words “God is the Greatest” on the north and south sides, while the Koran adorns the east and west sides. The spire of the tower features a spherical observation center at its base. The spire is capped with a shining mosaic gold crescent that weighs 35 metric tons. A number of cultural amenities are present in the upper levels of the tower, including a center for lunar observation and a cosmology museum.
Since a great deal of residents and guests in the tower perform prayers five times a day, innovative solutions were provided in the elevator systems that transport people in a smooth and efficient manner. Group control systems were implemented that adapt to the travel patterns of passengers, intelligently anticipating their general location and destination. Using this technology, up to 75,000 people can exit all seven buildings without issue.
22 August 2022
Tarek Hassan, Yehia El-Ezaby & Charles Malek, rector Dar Al Handasah Consultants (Shair and Partners)
This paper presents an overview of a process of optimizing concrete mixture for tall buildings, culminating in the design of the Iconic Tower, the key...

20 March 2020
CTBUH Research
This research paper undertakes a review of the 2012 report by the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat, “Tallest 20 in 2020: Entering the...

29 July 2019
Since humans first began constructing tall buildings, history has been cluttered with claims of all manner of “highest” records. In this study, we examine those...
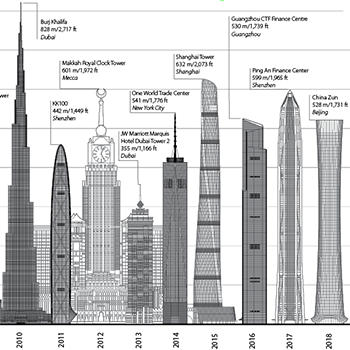
31 January 2019
CTBUH Research
In 2018, 143 buildings of 200 meters’ height or greater were completed. This is a slight decrease from 2017’s record-breaking total of 147, and it...
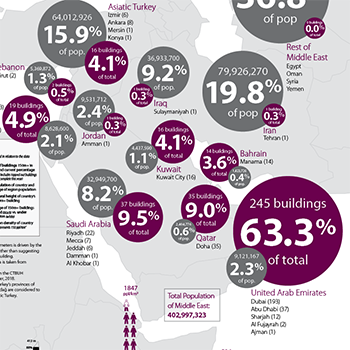
20 October 2018
CTBUH Research
The Middle East region is hosting its first CTBUH International Conference since 2008. In that year, there were 119 completed buildings of 150 meters or...

14 November 2013
CTBUH Research
Twenty years ago, the Middle East contained only one skyscraper over 150 meters in height. It is now estimated that by the end of 2015...

31 December 2012
Kevin Brass, Antony Wood & Marty Carver, CTBUH
For the first time in six years the number of tall buildings completed annually around the world declined as the effects of the global financial...

18 January 2012
Nathaniel Hollister & Antony Wood, CTBUH
Within this decade we will likely witness not only the world’s first kilometer-tall building, but also the completion of a significant number of buildings over...
28 November 2018
CTBUH has released a Tall Buildings in Numbers (TBIN) interactive data study examining the relationship between high-rise growth and population in the Middle East.
12 September 2017
CTBUH partnered with Guinness World Records to identify the commercial building with the fastest elevator speeds and longest vertical runs.
13 October 2016
The Council is pleased to announce the Top Company Rankings for numerous disciplines as derived from the list of projects appearing in 100 of the World’s Tallest Buildings.
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy