Filter by
This project is a redesign and replaced 2 World Trade Center (Previous)
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.

2 World Trade Center
Building
Canceled
Office
Composite
403.3 m / 1,323 ft
82
4
260,000 m² / 2,798,617 ft²
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Usually takes on the balance of the architectural effort not executed by the "Design Architect," typically responsible for the construction documents, conforming to local codes, etc. May often be referred to as "Executive," "Associate," or "Local" Architect, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Architect of Record" exclusively.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Usually takes on the balance of the architectural effort not executed by the "Design Architect," typically responsible for the construction documents, conforming to local codes, etc. May often be referred to as "Executive," "Associate," or "Local" Architect, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Architect of Record" exclusively.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The CTBUH lists a project manager when a specific firm has been commissioned to oversee this aspect of a tall building’s design/construction. When the project management efforts are handled by the developer, main contract, or architect, this field will be omitted.
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
7 April 2016 - Event
28 October 2015 - Event

15 April 2016 | New York City
Bjarke Ingels, BIG, discusses new building parameters and how they have influenced the design of two of New York City's most unique projects, 2 World...

26 October 2015
Stephan Reinke, Stephan Reinke Architects
This paper will reveal the importance of integrating the Ground Plane, Mid-Level and Rooftop Urban Public Spaces in the City. We will explore the NYLON...

15 April 2016 | New York City
Bjarke Ingels, BIG, discusses new building parameters and how they have influenced the design of two of New York City's most unique projects, 2 World...

27 October 2015 | New York City
With the rise of technological solutions, the practice of architecture is often divorced from the cultural, social, and environmental contexts where we build. Buildings have...

27 October 2015 | New York City
Bjarke Ingels of Bjarke Ingels Group is interviewed by Chris Bentley during the 2015 CTBUH New York Conference at the Grand Hyatt New York. Bjarke...

26 October 2015 | New York City
Gary Barnett, Extell Development Corporation; Ric Clark, Brookfield Properties; Joseph Moinian, Moinian Group; and Larry Silverstein, Silverstein Properties, discuss development in New York City and...

26 October 2015
Stephan Reinke, Stephan Reinke Architects
This paper will reveal the importance of integrating the Ground Plane, Mid-Level and Rooftop Urban Public Spaces in the City. We will explore the NYLON...
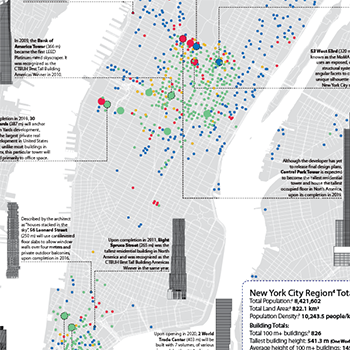
22 October 2015
CTBUH Research
A timeline of skyscraper completions in New York uncannily resembles the boom and bust cycles of the United States in the 20th and early 21st...
MarshallGerometta.jpg)
22 October 2015
New York 2015 Conference Special
To commemorate the CTBUH 2015 International Conference, some of the most prominent voices in the New York tall building industry today – all of whom...
7 April 2016
CTBUH New York Young Professional Committee held their annual Spring Social event at Bjarke Ingels Group's New York Office on April 7, 2016.
28 October 2015
CTBUH 2015 delegates toured 30 Park Place which will house the Four Seasons Hotel and Private Residences Downtown New York.
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy